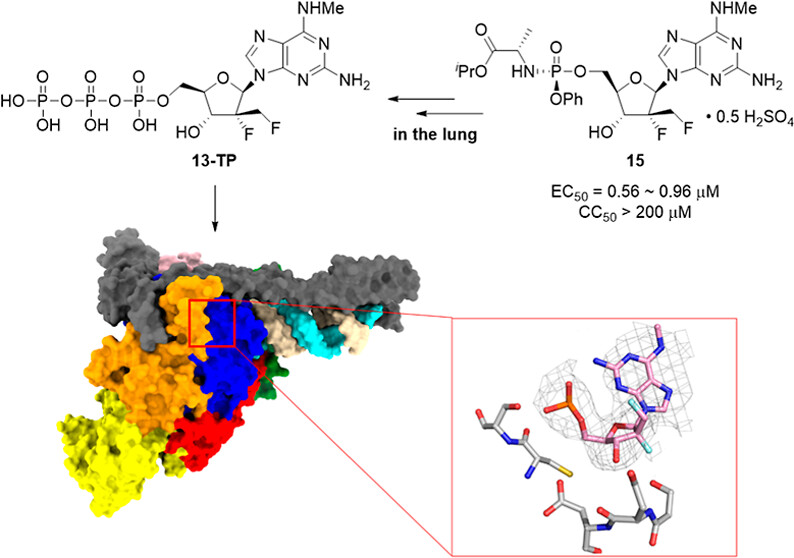
Recently, the team led by Academician Chang Junbiao from the National Key Laboratory of Innovative Medicine Development for Antiviral Infectious Diseases at HNU published a research paper entitled Discovery of a 2′-α-Fluoro-2′-β-C-(fluoromethyl) Purine Nucleotide Prodrug as a Potential Oral Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agent in Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. The PhD candidate from HNU Liang Lan is the co-first author (ranked first), while our university and Zhengzhou University serve as co-corresponding author institutions.
As variants of SARS-CoV-2 continue to emerge, the ongoing development of safe, effective, and convenient anti-SARS-CoV-2 medications remains essential. The team focused on the research and development of potential oral antiviral drugs targeting SARS-CoV-2 infection, designing and synthesizing a novel prodrug compound, 2′-α-Fluoro-2′-β-C-(fluoromethyl) purine nucleoside phosphoramidate proddrug compound 15. The corresponding bioactive nucleoside triphosphate (13-TP) effectively inhibited the in vitro RNA synthesis catalyzed by the SARS-CoV-2 central replication transcription complex (C-RTC). The structure of the C-RTC in complex with 13-TP was determined using cryo-electron microscopy. In vitro experiments showed that this compound exhibited powerful antiviral activity against the SARS-CoV-2 20SF107 strain (EC50 = 0.56±0.06 μM) and the Omicron BA.5 variant (EC50 = 0.96±0.23 μM), with low cytotoxicity. Moreover, the prodrug demonstrated good tolerance in rats, achieving high concentrations of 13-TP in the target organ (lungs) following a single oral dose of 40 mg/kg, along with a prolonged half-life. These findings provide strong support for the development of this compound as an oral anti-SARS-CoV-2 medication, potentially offering new therapeutic options for SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Academician Chang Junbiao’s team has long been dedicated to the research and development of novel nucleoside antiviral drugs targeting infectious diseases caused by viruses such as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Hepatitis B Virus (HBV), Hepatitis C Virus (HCV), Dengue Virus (DENV), Enterovirus (EV71), Zika Virus (ZIKV), Monkeypox Virus (MPXV), and SARS-CoV-2. Among them, Azvudine, as a new type of nucleoside antiviral drug independently developed in China with global patents, has been approved by the National Medical Products Administration for the treatment of HIV-1 infection and SARS-CoV-2 infection. The discovery of Azvudine and its new mechanism for combating HIV and SARS-CoV-2 was selected by the Ministry of Science and Technology as a significant achievement in the 13th Five-Year Plan China Basic Research Development Report. The development of Azvudine has also been included in the National Natural Science Foundation’s Medical Science 14th Five-Year Plan Discipline Development Strategy Research Report and featured in the 15th Anniversary Commemorative Collection of Outstanding Achievements Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation’s Medical Science Department. Recognized as the top ten scientific and technological innovation achievements in Henan Province over the past decade, Azvudine has been awarded two first prizes in Henan Provincial Technology Invention Awards. Currently, Academician Chang Junbiao is leading the clinical trials of three other category-1 new medicines, which are in phases I-III.
Paper Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02769?articleRef=test
(National Key Laboratory of Innovative Drug Development for Antiviral Infectious Diseases: Ma Junguo, Zhu Gongming)


 2025-02-25
2025-02-25



