Recently, the research team led by Professor Guo Haiming from HNU, in collaboration with the team led by Professor Wang Yang from Fudan University, have published a research paper entitled “Discovery of Novel Oxazolo[4,3-f]purine Derivatives as Antitumor Agents through PPIA Interaction” in the international pharmaceutical journal Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. Li Xianjia, a doctoral student of HNU, is the first author of the paper. Professor Guo Haiming, Associate Professor Hao Erjun, Professor Wang Yang from Fudan University, and Dr. Liang Yuru from Shanghai Jiao Tong University are the co-corresponding authors, and our university is the first corresponding unit. This research was sponsered by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province, and Pingyuan Laboratory.
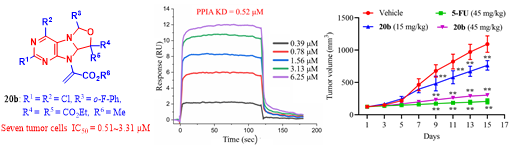
In the field of drug research and development, tricyclic purine nucleosides occupy an important position due to their unique structures. The research team designed and synthesized a series of tricyclic purine nucleoside compounds. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies showed that most of the synthesized tricyclic purine nucleoside compounds have moderate to potent antitumor activity. Among them, compound 20b exhibited significant antiproliferative activity against HCT116 cells, and its in vitro antiproliferative activity against tumor cells was superior to that of cisplatin, a clinically used antitumor drug. Mechanism studies revealed that compound 20b could significantly inhibit the migration and invasion of HCT116 cells and arrest the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase. Compound 20b increased the ROS level in HCT116 cells, leading to DNA damage, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inducing cell apoptosis, as well as affecting the expression levels of proteins related to the PPIA/MAPK signaling pathway. The results of drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) assay, cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA), and small interfering RNA (siRNA) experiment indicated that compound 20b targets PPIA. Mouse xenograft tumor experiments showed that compound 20b has good in vivo anti-colon cancer activity and low toxicity. These results suggest that compound 20b is an effective PPIA inhibitor-based antitumor compound, which is worthy of further in-depth research and development.
Paper Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02819
(Jiang Tao and Wang Manman from School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering)


 2025-03-20
2025-03-20



